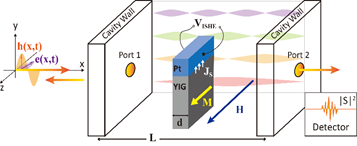
腔自旋波电子学(Cavity Magnonics):腔自旋波电子学是最近兴起的关于多自旋体系与共振腔相互作用的研究领域。它融合了自旋波电子学与光学,探索以自旋波为信息载体的系统与共振腔形成的杂化态,涉及光子与磁振子的复杂耦合及可能出现的量子效应。该方向的系列问题还包括具有PT-对称性的自旋波动力学,反铁磁动力与光子的强耦合,光磁耦合下的宏观法拉第旋转角,波导中随机磁片分布对光子局域性的影响,等。
生物磁学(Bio-Magnetism): 自然界有很多生物能够感知地球磁场, 比如帝王蝶, 鲑鱼, 龙虾, 海龟以及迁徙的鸟类等可以利用地磁场做到长途跋涉而不迷路。这种磁感受机制的生物物理起源如今还是一个未解之谜。 2016年北京大学谢灿研究组报道了一种磁受体蛋白Drosophila CG8198 (MagR) [S. Qin et al., Nat. Mater. 15, 217 (2016)。该蛋白通过多聚化组装形成了一个包含40个铁原子, 长度约为24纳米的棒状蛋白质复合物, 就像一根小磁棒具有南北极。然而, 这个结论随后受到了加州理工学院生物与生物工程系Markus Meister的质疑 [M. Meister, Elife 5, e17210 (2016)]。
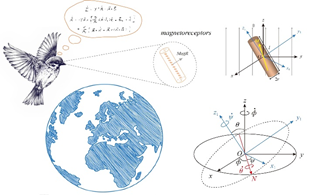
通过估算, Markus Meister指出40个铁原子磁矩与地球磁场(~25-65 μT)的耦合比室温下的热噪声小5个数量级, 因而随机涨落会彻底破坏磁矩的方向, 让磁蛋白失去指南针功能。我们研究发现, 原子尺度下的自旋-机械耦合, 也就是角动量在自旋自由度和刚体转动之间的相互转换, 会让磁蛋白获得很好的室温指南针能力。从随机Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert方程出发, 我们的理论计算表明, 考虑自旋-机械耦合之后, 室温下约有65%的磁矩会平行于地磁场的方向排列, 与此同时, MagR内部小磁棒绕自身长轴的转动角频率会达到1011 rad/s。我们的结果为澄清MagR热学性质的争议提供了一条途径, 也将激发人们对原子尺度下自旋-机械耦合研究的广泛兴趣。
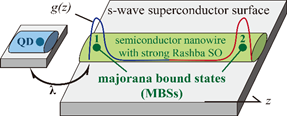
量子输运(Quantum Transport): 量子输运中的非马尔科夫效应以及Majorana费米子的探测问题。
自旋波动力学(Magnonics):本质上结合了波与磁性的问题,主旨在于研究纳米结构中的自旋波的行为,利用磁矩进动形成的自旋波来实现自旋角动量传输;
自旋热电子学(Spin Caloritronics):研究主要关于温度梯度作用下电荷,自旋,热的输运以及它们之间的相互作用,包括自旋塞贝克效应(spin Seebeck effect),自旋温度弛豫等。
发表论文
21. Yunshan Cao and Peng Yan, "Exceptional magnetic sensitivity of PT-symmetric cavity magnon polaritons", Phys. Rev. B 99, 214415 (2019). (Corresponding author)
20. X. Wang, X. S. Wang, C. Wang, H. Yang, Y. Cao and P. Yan, "Current-induced skyrmion motion on magnetic nanotubes", Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 52, 225001 (2019).
19. Z. Wang, B. Zhang, Y. Cao, and P. Yan, "Probing the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya Interaction via the Propagation of Spin Waves in Ferromagnetic Thin Films", Phys. Rev. Applied 10, 054018(2018).
18. Z.-X. Li, C. Wang, Y. Cao, and P. Yan, "Edge states in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice of massive magnetic skyrmions", Phys. Rev. B 98, 180407(2018).
17. H. Yang, C. Wang, T. Yu, Y. Cao, and Peng Yan, "Antiferromagnetism Emerging in a Ferromagnet with Gain", Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 197201(2018). (Corresponding author)
16. C. Wang, Y. Cao, X. R. Wang, and P. Yan, "Interplay of wave localization and turbulence in spin Seebeck effect", Phys. Rev. B 98, 144417 (2018).
15. H. Yang, C. Wang, X. Wang, X. S. Wang, Y. Cao, and P. Yan, "Twisted skyrmions at domain boundaries and the method of image skyrmions", Phys. Rev. B 98, 014433 (2018).
14. Yunshan Cao and Peng Yan, "Role of atomic spin-mechanical coupling in the problem of a magnetic biocompass", Phys. Rev. E 97, 042409 (2018). (Corresponding author)
13. B. Zhang, Z. Wang, Y. Cao, P. Yan , X.R. Wang, "Eavesdropping on spin waves inside the domain-wall nanochannel via three-magnon processes", Phys.Rev.B 97,094421(2018). (Corresponding author)
12. W. Yang, Y. Cao, P. Yan , "Photonic orbital angular momentum transfer and magnetic skyrmion rotation", Opt. EXPRESS 26(7), 8778 (2018).(Corresponding author)
11. P. Yan, Y. Cao, J. Sinova, "Thermodynamic Magnon Recoil for Domain Wall Motion", Phys. Rev. B 92, 100408(R) (2015).
10. B. Z. Rameshti, Y. Cao, G. E. W Bauer, "Magnetic spheres in microwave cavities", Phys. Rev. B 91, 214430 (2015).
09. Yunshan Cao, Peng Yan, Hans Huebl, Sebastian Goennenwein, Gerrit E.W. Bauer, " Exchange Magnon-Polaritons in Microwave Cavities", Phys. Rev. B 91, 094423 (2015).
08. L. Xu, Y. Cao, Xin-Qi Li, Y. Yan, and S. Gurvitz, "Quantum transfer through a non-Markovian environment under frequent measurements and Zeno effect", Phys. Rev. A 90, 022108 (2014).
07. P. Wang, Y. Cao, M. Gong, S.-S. Li, Xin-Qi Li, "Demonstrating nonlocality-induced teleportation through Majorana bound states in a semiconductor nanowire", Phys. Lett. A 378, 937 (2014).
06. P. Wang, Y. Cao, M. Gong, G. Xiong, X. Li, "Cross-correlations mediated byMajorana bound states", EPL103, 57016(2013).
05. Peng Yan, Akashdeep Kamra, Yunshan Cao, and Gerrit E.W. Bauer, "Angular and Linear Momentum of Excited Ferromagnets", Physical Review B 88, 144413 (2013).
04. Yunshan Cao, Peiyue Wang, Gang Xiong, Ming Gong and Xin-Qi Li, "Probing the existence and dynamics of Majorana fermion via transport through a quantum dot", Physical Review B 86, 115311 (2012).
03. Yunshan Cao, Luting Xu, Xin-Qi Li, "Non-Markovian Transmission through Two Quantum Dots Connected by a Continuum", Physics Letters A 376, 2989 (2012).
02. Wenxi Lai, Yunshan Cao, Zhongshui Ma, "Current-oscillator correlation and Fano factor spectrum of quantum shuttle with finite bias voltage and temperature", J.Physics: Condensed Matter 24, 175301 (2012).
01. Y. Ye, Y. Cao, Xin-Qi Li, S. Gurvitz, "Decoherence and the retrieval of lost information", Phys. Rev. B 84, 245311 (2011).
大会邀请报告
2015 德国 Ringberg Castle:Beyond! Materials and Devices beyond CMOS 邀请报告
2015 香港 Gordon Research Conference - Spin Dynamics In Nanostructures 邀请报告
2015 香港 Gordon Research Seminar 主席






